dyson_equalizer.plots module#
The dyson_equalizer.plots module provides functions to create useful plots
- dyson_equalizer.plots.plot_mp_density(eigs: ndarray, gamma: float, show_only_significant: int = None, show_only_significant_right_margin: float = 0.3, matrix_label: str = 'X', bins: int | str | Sequence = 'sqrt', ax: Axes | None = None) None[source]#
Plots the density of eigenvalues of the covariance matrix and compares to the Marchenko-Pastur distribution
This function assumes the input are the eigenvalues of a covariance matrix of a random matrix whose entries have variance 1. These eigenvalues follow the Marchenko-Pastur distribution.
- Parameters:
- eigs: (n) numpy.array
The array of eigenvalues (e.g. of a covariance matrix) to plot
- gamma: float
The ratio between the dimensions of the matrix (between 0 and 1)
- show_only_significant: int, optional
Set this value to show only a small number of significant eigenvalues (defaults to None) This option is useful is some of the signal eigenvalues are much bigger than the noise. Set to zero to show only significant eigenvalues within the margin indicated by show_only_significant_right_margin
- show_only_significant_right_margin: float, optional
Specifies the size of the right margin (defaults to 0.3) from the largest eigenvalue selected by the show_only_significant option
- matrix_label: str, optional
The name of the matrix that will be used as label (defaults to
X)- bins: int or sequence or str, default: ‘sqrt’
The bins parameter used to build the histogram.
- ax: plt.Axes, optional
A matplotlib Axes object. If none is provided, a new figure is created.
See also
dyson_equalizer.algorithm.marchenko_pasturmatplotlib.pyplot.Axes.hist
Examples
We generate a random matrix X of size (100, 1000) and show that the eigenvalues of the covariance matrix Y = ¹⁄ₙXXᵀ follow a Marchenko-Pastur distribution.
import numpy as np from dyson_equalizer.plots import plot_mp_density m, n = 100, 1000 X = np.random.normal(size=(m, n)) Y = X @ X.T / n eigs = sorted(np.linalg.eigvals(Y), reverse=True) plot_mp_density(eigs, gamma=m/n)
(
Source code,png,hires.png,pdf)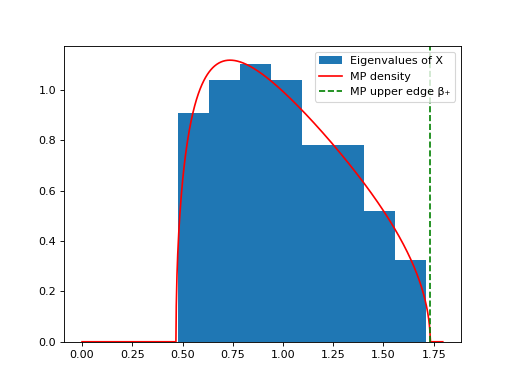
Eigenvalues plot of a random matrix#
- dyson_equalizer.plots.plot_mp_eigenvalues(eigs: ndarray, gamma: float, eigenvalues_to_show: int = 100, log_y: bool = True, matrix_label: str = 'X', ax: Axes | None = None) None[source]#
Plots the eigenvalues of the covariance matrix and compares to the Marchenko-Pastur threshold
This function assumes the input are the eigenvalues of a covariance matrix of a random matrix whose entries have variance 1. These eigenvalues follow the Marchenko-Pastur distribution.
- Parameters:
- eigs: (n) numpy.array
The array of eigenvalues (e.g. of a covariance matrix) to plot
- gamma: float
The ratio between the dimensions of the matrix (between 0 and 1)
- eigenvalues_to_show: int, optional
The number of eigenvalues to show in the plot (defaults to 100)
- log_y: bool, optional
Whether the y-axis should be logarithmic (defaults to True)
- matrix_label: str, optional
The name of the matrix that will be used as label (defaults to
X)- ax: plt.Axes, optional
A matplotlib Axes object. If none is provided, a new figure is created.
Examples
We generate a random matrix X of size (100, 1000) and show that the eigenvalues of the covariance matrix Y = ¹⁄ₙXXᵀ follow a Marchenko-Pastur distribution.
import numpy as np from dyson_equalizer.plots import plot_mp_eigenvalues m, n = 100, 1000 X = np.random.normal(size=(m, n)) Y = X @ X.T / n eigs = sorted(np.linalg.eigvals(Y), reverse=True) plot_mp_eigenvalues(eigs, gamma=m/n)
(
Source code,png,hires.png,pdf)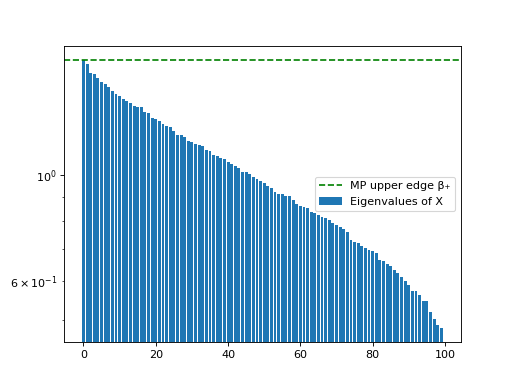
Eigenvalues plot of a random matrix#